Uygafly Personalized Belt Bag for Women Girls - Fashion Mini Waist Packs with Adjustable Strap - Trendy Travel Fanny Pack Crossbody Bags with Initial Letter - Teen Gifts | Black,S
$19.99 (as of February 10, 2025 20:51 GMT +00:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Introduction
Server Manager is a powerful tool used in Windows Server operating systems that allows administrators to manage various server roles, features, and configurations from a single interface. While it provides convenient access to important server management tasks, some users may find it unnecessary to have Server Manager launching at startup, especially on servers with specific roles that do not require frequent changes. In this article, we will explore how to disable Server Manager at startup to streamline the server’s boot process and reduce unnecessary resource consumption.
Reasons to Disable Server Manager at Startup
There are several reasons why you might want to disable Server Manager from launching at startup:
Simplifying the Boot Process
In production environments, minimizing the number of startup applications can lead to faster boot times. Disabling Server Manager can help streamline the server’s boot process.
Resource Conservation
Server Manager consumes system resources, including memory and CPU usage, during its operation. Disabling it at startup can free up these resources for other critical services.
Specialized Server Roles
In cases where a server has a specific and dedicated role, such as a domain controller or web server, administrators might prefer to disable Server Manager since they may not need its features regularly.
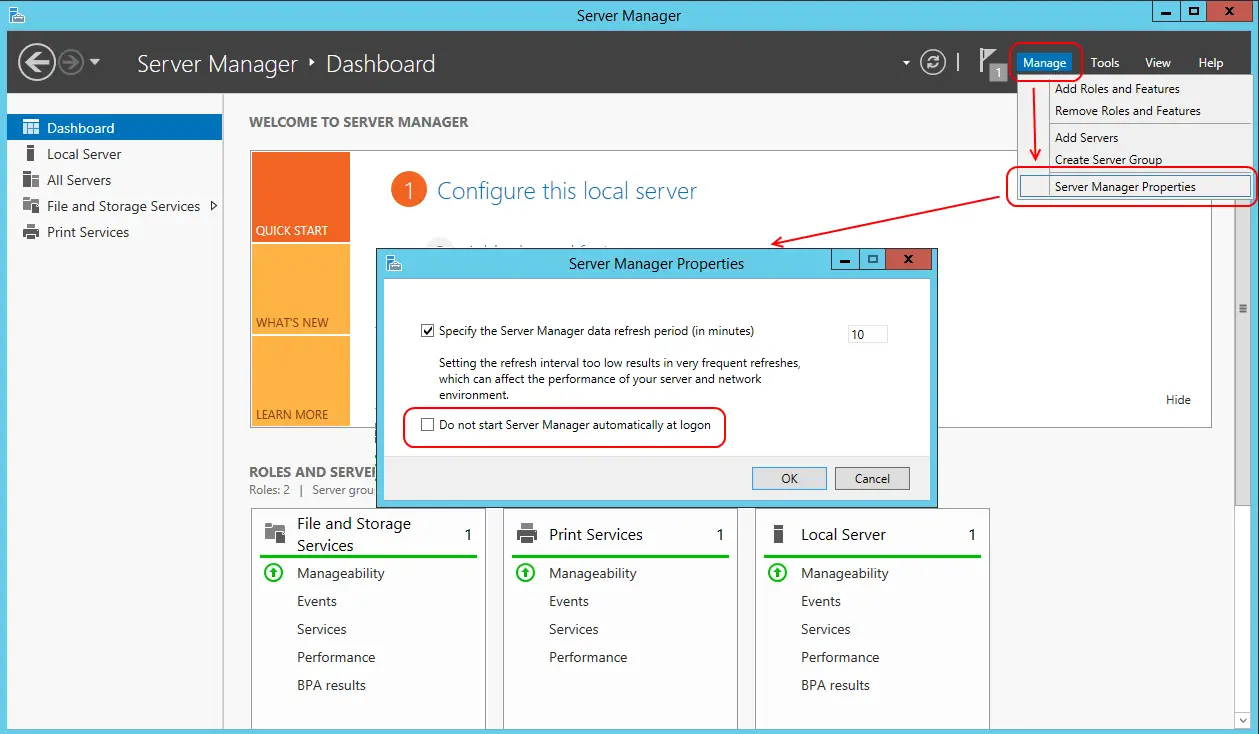
Easiest Method:
The easiest way to disable the server manager pop-up is by disabling it on the server manager properties
- Open the server manager dashboard and go to Manage and click Server Manager Properties
- Check the tick mark on the “do not start server manager automatically at logon” check box and click OK to save the settings
Group Policy Method:
We can even disable via group policy by following the below method.
- Open group policy management [gpupdate.msc] console
- Navigate to Computer Configuration → Administrative templates → System → Server Manager
- Open the Server Manager folder and double click “Do not display server manager automatically at logon” set the field to Enabled and click OK to save the settings
Disabling Server Manager via Registry Editor
If Group Policy Editor is not available, the Registry Editor can be used to disable Server Manager:
Step 1: Open Registry Editor
Press “Windows + R” on your keyboard to open the Run dialog. Type “regedit” and press Enter to launch the Registry Editor.
Step 2: Navigate to the Server Manager Key
In the Registry Editor, go to the following location:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\ServerManager
Step 3: Disable Server Manager
Find the “DoNotOpenAtLogon” entry on the right pane, double-click it, and set its value to “1.”
Automating Server Manager Disablement for Multiple Servers
For large-scale server management, PowerShell scripts can be utilized to automate the process of disabling Server Manager across multiple servers.
Impact of Disabling Server Manager
Disabling Server Manager does not affect any installed server roles, features, or configurations. It only prevents the application from launching automatically at startup.
Best Practices for Server Manager Management
While disabling Server Manager can be beneficial in certain scenarios, it is essential to follow these best practices:
Regularly Check Server Manager
Even though Server Manager may not start at logon, administrators should periodically open it to check for critical updates or to manage specific roles when necessary.
Use Task Scheduler Sparingly
Avoid using Task Scheduler to disable Server Manager if there are other viable methods available, as Task Scheduler might complicate the process and potentially cause unintended consequences.
Keep an Eye on Server Performance
Monitor server performance to ensure that disabling Server Manager has a positive impact on resource utilization and overall system performance.
Conclusion
Disabling Server Manager at startup can be a valuable step in optimizing the boot process and conserving system resources on dedicated servers. By following the outlined methods, server administrators can choose the most suitable approach for their specific environments and efficiently manage server roles and configurations.
FAQs
1. Can I still manually launch Server Manager after disabling it at startup?
Yes, you can still open Server Manager manually by searching for it in the Start menu or using the “servermanager.exe” command.
2. Does disabling Server Manager remove any installed server roles or features?
No, disabling Server Manager does not affect any installed server roles, features, or configurations. It only prevents the application from starting automatically at logon.
3. Can I re-enable Server Manager after disabling it?
Yes, you can re-enable Server Manager by following the same steps used to disable it. Simply choose the appropriate option to start Server Manager automatically at logon.

Greetings! I am Ahmad Raza, and I bring over 10 years of experience in the fascinating realm of operating systems. As an expert in this field, I am passionate about unraveling the complexities of Windows and Linux systems. Through WindowsCage.com, I aim to share my knowledge and practical solutions to various operating system issues. From essential command-line commands to advanced server management, my goal is to empower readers to navigate the digital landscape with confidence.
Join me on this exciting journey of exploration and learning at WindowsCage.com. Together, let’s conquer the challenges of operating systems and unlock their true potential.